The teeth aren’t the only important part of the mouth; the gums are equally as important yet often overlooked. Without the right oral care, it’s possible that your gums will succumb to periodontal disease. The consequences of periodontal disease can be devastating to your mouth. Gum tissue pulls away from the bone, bone tissue breaks down, teeth fall out, and so much more. Fortunately, there is now a simple, painless, and effective gum disease treatment that replaces surgery and restores the mouth back to health: Laser Assisted New Attachment Procedure (LANAP). [Read more…]
Implant Retained Dentures
 Unsecured dentures are an old fashioned solution for people who have lost all their teeth. Unfortunately, you may find that wearing unsecured dentures can be painful, inconvenient and awkward. Such dentures make it difficult to chew a variety of foods, which can stop you from eating many of the foods you once enjoyed. Wearing dentures may also affect how you pronounce words, and therefore the way you speak. A conventional denture has an acrylic palate that also hinders your ability to taste the foods that you once loved.
Unsecured dentures are an old fashioned solution for people who have lost all their teeth. Unfortunately, you may find that wearing unsecured dentures can be painful, inconvenient and awkward. Such dentures make it difficult to chew a variety of foods, which can stop you from eating many of the foods you once enjoyed. Wearing dentures may also affect how you pronounce words, and therefore the way you speak. A conventional denture has an acrylic palate that also hinders your ability to taste the foods that you once loved.
A variety of modern dental implant-based tooth replacement solutions are available. Any of these solutions can dramatically improve your quality of life; such as enabling proper chewing and speaking, increasing comfort and self-confidence, and encouraging the consumption of a wider variety of foods.
Benefits
People who have suffered with dental problems may ultimately have to consider getting dentures. While the traditional dentures that are removable have been the choice for many people, implant retained dentures are becoming the new choice.
Dentures are simply a restoration for missing teeth. You can have a partial set or full set of dentures. They are generally made from a plastic base, with artificial teeth positioned on the frame. This is a replacement for natural teeth, not just for cosmetic reasons. Missing teeth can impact ability to speak clearly, interfere with eating, and can ultimately have negative health consequences. Dentures are used to eliminate these problems.
Another problem with missing teeth is the impact it has on bone structure. Implant retained dentures not only look natural, but it will make your smile beautiful again. It will keep your facial structure younger looking, because the teeth help hold everything in place.
Initial Consultation
Before any work gets done, the dentist will review your individual case: Study medical and dental records; take x-rays; take impressions of your teeth and gums. Where necessary, you may even need to go for a CT scan. The main purpose of the initial consultation is to determine the quality and quantity of your bone as well as the prime location for placing the implants. The impressions will also be used to make models of your teeth structure upon which the dimensions of the temporary denture are based.
Procedure #1
This session generally involves making an incision in the gums and placing the implants in the jawbone. After the implant is placed into the hole (drilled in the bone), the dentist will stitch up the incision. The temporary denture is then positioned in such a way that no direct pressure is placed on the implants – a soft reline may be necessary to take the pressure off your gums.
The timing of the second procedure depends on whether the implants were placed in the upper (5-6 months later) or lower jaw (3-4 months later). This period is to allow the bone and implants to biologically ‘fuse’ together in a process known as osseointegration.
Procedure #2
Following the osseointegration process, the implant is ready for the second procedure. The dentist would confirm whether the implants have become fused with the bone by taking an x-ray. In this follow-up procedure, a small incision would be made in the gum to expose the tops of the implants.
Once the implants have become fused with the bone, the second procedure can be scheduled. Your dentist will confirm whether the implant is ready for the second procedure by taking an X-ray. This surgery is simpler than the first, which involves making a small incision in your gum to expose the tops (heads) of the implants.
The dentist would then place a round piece of metal, known as a collar or healing cap, on the head of each exposed implant. The collar, used to hold the gums separate from the implant head, will remain in place for 10-14 days. In the meantime, the temporary denture may be adjusted or given another reline. The healing caps will be replaced with regular abutments about two weeks after the second procedure. By now, your gums would have healed and your dentist is able to take impressions of your gum tissue and abutments. The model of your jaw and abutments is then made to fabricate the permanent denture.
Try-In and Insertion
At this final stage, usually in month 5 or 7 – depending on whether a denture needs to be made – you are ready to have the initial try-in of the new denture. Once the metal bar is placed on the abutments and fits together with the dental framework properly, the artificial teeth would be temporarily placed on the framework in wax. If everything checks out – with the whole denture tried in your mouth – the teeth would then be permanently lodged in the denture framework. Depending on the type of implant-supported denture you have selected, either the ball or bar attachments will be secured at this juncture.
You will have to return for another visit to insert the completed denture. The denture may either be snapped into the ball attachments or clipped onto the bar.
There are different types of implant treatments with differing time frames and procedures. Generally speaking, a standard implant treatment would require two procedures: One to place the implants into the jawbone, and second, to expose the top of the implants so that the implant-supported denture may be affixed to them. The second procedure is normally performed three to six months after the first one.
It is also possible to use a one-stage procedure, in which the implants as well as supporting bar are placed in a single step. Both types of treatments enjoy a healthy success rate.
The implants are usually placed in the area of the jawbone with a higher bone mass – typically at the front of your mouth. The front jaw is also preferred because it does not have many nerves or structures that may complicate the implant placement.
The time it takes to complete the treatment depends on different factors, including: Type of implant used; whether the treatment is for the upper or lower jaw; if bone grafting is required; number of implants, etc. For standard implants, the process can take anywhere between 5 months to a year or more.
Do I Need a Temporary Denture?
The temporary denture is necessary only if you are not already wearing a complete denture for your missing teeth. As the name suggests, the temporary denture is used as a placeholder while you wait for your final implant-supported denture to be made. It also serves as a back-up prosthesis in the unlikely event the final denture is damaged.
Implant retained dentures are more secure than traditional dentures. Removable dentures must be held in place by a bonding agent, and are traditionally known for coming loose when you eat certain foods. Implants are held in place more securely and are overall more reliable.
- Implant dentures are also more comfortable for the wearer. Most people report they don’t even feel like they have dentures in.
- Implant retained dentures also prevent the wearer from experiencing sore spots and pressure points commonly associated with removable dentures.
- When wearing implanted dentures, it prevents further bone loss that occurs from missing teeth. This also allows the facial structure to stay the same, and keeps your mouth healthier.
Your Dentist’s Healthy Teeth Holiday Wish List
 Santa’s not the only one making his list and checking it twice this holiday season. With the influx of candy and sweets during the holidays, dentists have a few wishes of their own when it comes to keeping your teeth healthy and strong through the holiday season.
Santa’s not the only one making his list and checking it twice this holiday season. With the influx of candy and sweets during the holidays, dentists have a few wishes of their own when it comes to keeping your teeth healthy and strong through the holiday season.
Make Your Sweets Sugar-Free
You love sugar – and so do the bacteria that live in your mouth that cause tooth decay. When you eat sugary foods, cavity-causing bacteria produce acids that eat away at your teeth. So, pick sweets of the sugar-free variety, which will provide less food for hungry bacteria and fewer acids on your teeth.
If you are really hoping to give your teeth a boost while also enjoying candy, consider looking for treats sweetened with xylitol. “Xylitol can help with reducing plaque buildup. You might consider it as a sweetener as opposed to the blue and pink packages. Xylitol is a U.S. Food and Drug Administration-approved sugar alcohol that has been shown to reduce the amount of Streptococcus mutants bacteria known to cause cavities in your mouth. The compound is as sweet as sugar and is commonly included in chewing gum, mints and cereals. If you are a baking enthusiast, you also can use xylitol instead of sugar without having to change the amount included in your recipe. The catch is that xylitol has to be present in significant enough levels to prevent decay. Read label listings. If xylitol is listed as the first ingredient, the food likely contains enough to prevent decay, according to the California Dental Association.
Pop a Stick of Gum Post-Meal
The benefits of sugar-free candy extend beyond the fact that they don’t contain sugar. Sugar-free gums and candies also help produce extra saliva that can swish away bacteria and plaque.
“The bacteria that cause decay usually flourish in a dry-mouth environment, which leads to increased incidence of tooth decay. When you pop in a piece of sugar-free gum after a meal, you also can un-stick food material. The gum clears bacteria and other sticky foods out of the mouth and off your teeth.
You don’t have to chew gum for long to reap its benefits. About 20 minutes post-meal should be sufficient, according to the ADA. Look for gums labeled with the ADA Seal, which indicates the gum contains non-cavity causing sweeteners such as aspartame, sorbitol or mannitol.
Enjoy Dark Chocolate Delights
Diabetes, heart disease and high blood pressure – these aren’t just the enemies of your heart. Studies have shown an association between these diseases, their treatments and dental health, too. That’s why if you are a chocoholic, it’s best to opt for dark chocolate because it’s packed with flavonoids, or compounds that help to protect your heart. Sadly, milk chocolate and white chocolate won’t offer you the same protective benefits. When you’re asking a loved one for a dark chocolate bar, ensure it is at least 60 percent or more real cocoa. Otherwise, you won’t reap the heart-protective benefits and you will add a lot of calories and fat to your diet.
Keep Sticky Foods Out of Your Stocking
Gummy bears and taffy may be tasty treats, but the sticky stuff is not your friend. This goes not only for chewy candies, but also dried fruits such as cranberries, which are a common holiday staple. Not only do chewy candies and dried fruits make for a chewier eating experience that works your jaw and teeth, those particles tend to linger longer on your teeth, increasing the cavity-causing potential. For a child with braces, chewy candies can mean a holiday trip to the dentist.
If you can’t resist the pull of a delicious gummy bear, have your fill at one sitting. “Eating candies all day long will cause more problems (in the oral cavity) than eating the whole bag at one time,”he says. It takes saliva some time to penetrate the mass, so if you keep exposing your teeth to the sugar, you are more likely to experience decay.
Dental Pain
Toothaches will make anyone feel miserable. Some reasons for toothaches include:
Misaligned Teeth or Impacted Wisdom Teeth
 Teeth that are misaligned can press against others, pushing them out of line as well, resulting in aches and pains. Impacted wisdom teeth, also known as wisdom teeth that have failed to break through the gum line, can also be extremely painful as they fester below the gum line and sometimes push against other teeth. These issues should be brought to the attention of your dentist, if they haven’t been addressed yet. For misaligned teeth, an orthodontic solution will likely be proposed, such as braces, and surgery will be needed to fix impacted wisdom teeth.
Teeth that are misaligned can press against others, pushing them out of line as well, resulting in aches and pains. Impacted wisdom teeth, also known as wisdom teeth that have failed to break through the gum line, can also be extremely painful as they fester below the gum line and sometimes push against other teeth. These issues should be brought to the attention of your dentist, if they haven’t been addressed yet. For misaligned teeth, an orthodontic solution will likely be proposed, such as braces, and surgery will be needed to fix impacted wisdom teeth.
Improper Brushing or Flossing
Very often people do not pay attention to the pressure they are using when they brush and floss their teeth and end up pressing much too hard. This results in irritated, inflamed, and bleeding gums. If extreme pressure like this is constantly used, it can cause gums to recede and can make teeth unstable, resulting in more pain. Consult your dentist about proper brushing techniques and be sure to only use soft bristled toothbrushes.
Teeth Grinding
Teeth grinding, or bruxism, is a very common reason for tooth, jaw, neck, and related muscle pain. People who grind their teeth generally do so while they’re sleeping or during stressful situations. Excessive teeth grinding involves violently clenching the jaw and grinding the top and bottom teeth back and forth against each other.
This can result in sore jaw bones and joints, headaches, and even cracked or chipped teeth, all of which are very painful. The best course of action to treat bruxism is to have a custom mouth guard made that is worn while sleeping to relieve the stress put on teeth and the jaw.
Damaged Fillings or Dental Sealants
Dental fillings that cover deep pits, grooves, or fractures in teeth often protect vulnerable parts of the tooth. When these protectants are damaged, the sensitive parts of teeth are exposed to extreme temperatures, food particles, and bacteria. This can result in a pain that is anything from a dull ache to a sharp, piercing sensation. If you have a damaged filling or sealant, be sure to book an emergency appointment with your dentist to have it fixed before the vulnerable parts of your tooth suffer further damage or decay.
Temperature Sensitivity
If you are experiencing sharp tooth pain during, or very soon after, eating or drinking something that is cold or hot, this is typically associated with tooth sensitivity. This can mean that your tooth enamel has worn down and your tooth’s dentin (the layer where the tooth’s nerves lie) is exposed, or can be a result of recent teeth whitening. To help protect these nerves and shelter them from extreme temperatures, try a toothpaste made for sensitive teeth. Consult your dentist for recommendations and further treatment options.
Tooth Fractures
Teeth can be cracked or chipped in many different ways, whether it’s through a fall, playing sports, or biting down on something hard or sticky. If you are feeling pain in a fractured tooth, that means that the fracture has made its way to the middle of the tooth where the nerve endings are and can result in excruciating pain.
This may not happen as soon as the tooth is chipped or damaged, but can develop over time as the tooth damage worsens. This is why all fractures and chips should be attended to by your dentist as soon as possible and before they have the chance to worsen.
Gum Disease
Gum disease is characterized by a dull pain in the mouth, red, bleeding gums, and also sometimes tooth pain. A common cause of this is the oral bone and gums becoming inflamed. If left untreated, teeth, gums, and bones could be damaged or lost, and surgical measures may have to be taken to rid the mouth of infection.
Tooth Abscess
When tooth decay advances to the point of affecting the root beneath the visible tooth there is a high chance that the root and the surrounding tissue have become infected. This will result in a widespread pulsating pain that may make it hard to determine which exact tooth is the culprit of the pain. This is a very serious issue and needs to be professionally dealt with as soon as possible as it can result in bone and tissue loss. Which, obviously, is no fun at all.
Tooth Decay
The most common reason for a painful toothache is plain old tooth decay. Sure, it might not be all that exciting or new, but it’s something that can affect any of us.
For the tooth and the surrounding area to hurt, the decay in the tooth would have to be significant enough to reach the inner layer of the tooth, a layer called the dentin. Once the dentin is damaged the tooth becomes very sensitive and a cavity, or carie, has developed.
If the pain becomes less of an ache and more of a sharp pain, the tooth decay may have reached the center of the tooth. This results in a very intense pain that makes it difficult to carry on with daily life. These issues need to be addressed as soon as possible as they are not only painful but can quickly lead to bigger dental issues.
If you’re experiencing any of these symptoms described above and have read through this whole list trying to figure out what might be wrong – call your dentist today. A simple examination can determine what’s going on, and the sooner you do it the better. Delaying can make a simple problem grow into a larger one just from neglect.
So don’t delay and don’t be scared! If going to the dentist makes you anxious, ask about sedation. There are multiple varieties available, and it’s perfectly normal to be nervous (some estimates say up to 80% of people suffer from dental fear!).
All About Dentures
 Dentures are artificial teeth and gums that are formed to your mouth and created by your dentists to replace lost or removed natural teeth. Dentures can either be full or partial, meaning they can either replace all teeth on either the top or bottom gum line, or just a few that are missing. Regardless of what kind of dentures you may need, they will be custom designed to fit your mouth, and visually matched to your existing teeth.
Dentures are artificial teeth and gums that are formed to your mouth and created by your dentists to replace lost or removed natural teeth. Dentures can either be full or partial, meaning they can either replace all teeth on either the top or bottom gum line, or just a few that are missing. Regardless of what kind of dentures you may need, they will be custom designed to fit your mouth, and visually matched to your existing teeth.
Dentures Then vs. Dentures Now
In the past, the artificial teeth that make up dentures were made out of porcelain or plastic, but more modern dentures are generally made out of a hard resin. The materials used to make denture teeth are known to be more fragile than natural teeth and can easily chip or crack if dropped or otherwise uncared for. This material also wears down much quicker than natural teeth and thus must be replaced with a new set of dentures every five years or so.
The supporting structure of dentures that holds the artificial teeth in place and resembles the natural gum line is often made out of a similar resin used for the teeth, or a more flexible polymer material that fits snugly on the natural gum line.
Dentures not only improve the appearance of a smile that has multiple missing teeth, but they also keep the structure of the mouth sound by supporting the structures around the cheeks and lips. Dentures also make it possible to eat foods that require chewing, making it possible to keep your diet the same and ensure that you are properly nourished. Lastly, dentures are a viable solution to replace teeth that are causing serious pain and oral health issues, such as those with rotted roots or severe damage. Having dentures fitted means that troublesome teeth are eliminated and replaced with a strong and beautiful alternative.
Partial Dentures
Partial dentures are often used instead of other tooth replacement methods when the surrounding natural teeth are not strong enough to support structures such as dental bridges, or when more than one or two teeth are missing.
The partial dentures are fitted to the part of the gum line that they will sit on, and fasten to nearby natural teeth to keep from falling out of place. They are not permanently fastened, however, and can be easily taken out at any time for cleaning and while sleeping.
Full Dentures
Full dentures, otherwise known as complete dentures, are dentures that replace all of your natural teeth. You can have them fitted for your top or bottom gum line, and are held in place by suction and/or the help of an oral adhesive. Just like partial dentures, they are easily removable.
Immediate Dentures and Overdentures
There are some other kinds of full and partial dentures that differ from traditional permanent dentures including a type called immediate dentures. These dentures are created before the teeth that are being replaced with dentures have been removed and are used immediately after tooth extraction and during the healing process, which can be up to six months long. These dentures can be more easily refitted than permanent dentures to accommodate for mouth changes as the swelling in the gums and jaw subsides while healing. The immediate dentures will be disposed of once the healing process is complete and your mouth is ready for permanent dentures.
Overdentures are an alternative that can be used if traditional dentures prove to be extremely uncomfortable or if you have a few natural teeth left. Overdentures are fitted over the roots of natural teeth and either rest on these or on dental implants, if there are no natural teeth to fit over. Some find this type of denture more comfortable and they are also easily removable.
Implant-Supported Dentures
As the name seems to imply, these are dentures which are anchored by dental implants. A dental implant is a permanent fixture that is anchored to the jawbone and can be used to replace any number of teeth. They’re comprised of the implant itself, a metal post (usually titanium), and a custom crown which looks just like a natural tooth.
Implant-supported dentures have a couple of different ways in which they can attach, but should be cared for and treated like traditional dentures. It’s more common to have them done on the lower jaw since the upper has fewer problems with fitting securely, but plenty of people have implants on both.
How to Clean Dentures
Regardless of what kind of dentures you may have, all dentures need to be cleaned daily, just like regular teeth. Even though dentures are made up of artificial teeth, bacteria, plaque, and tartar still build up on them and can harm existing teeth and gums.
To clean your dentures, take them out of your mouth and run clean water over them to dislodge any food particles that may be stuck between teeth, along the gum line, or underneath the structure. Then brush the dentures all over with a denture brush or very soft toothbrush using a mild soap or denture cleaner. Be sure not to use any other cleaners, regular toothpaste, or electric toothbrushes as these are all too abrasive and can damage and wear away the denture materials. After cleaning, make sure to rinse them well.
While your dentures are out of your mouth, be sure to clean your gums and any natural teeth with a very soft and wet toothbrush and fluoridated toothpaste if needed. If your toothbrush is too harsh, wrap your finger in a wet, soft washcloth and gently rub your gums, making sure to cover all surfaces.
Preserving Your Dentures
Always remove your dentures before sleeping to avoid damaging them, dislodging them, and to give your gums some time to relax. Submerge your dentures fully in warm, but not hot, water to keep them from drying out and becoming misshapen. Only use denture soaking solution if your dentures do not have metal components as the solution can tarnish the metal.
Bruxism (Teeth Grinding)
 Bruxism (BRUK-siz-um) is a condition in which you grind, gnash or clench your teeth. If you have bruxism, you may unconsciously clench your teeth together during the day, or clench or grind them at night (sleep bruxism). Sleep bruxism is considered a sleep-related movement disorder.
Bruxism (BRUK-siz-um) is a condition in which you grind, gnash or clench your teeth. If you have bruxism, you may unconsciously clench your teeth together during the day, or clench or grind them at night (sleep bruxism). Sleep bruxism is considered a sleep-related movement disorder.
Mild bruxism may not require treatment. However, in some people, bruxism can be frequent and severe enough to lead to jaw disorders, headaches, damaged teeth and other problems.
Because you may have sleep bruxism and be unaware of it until complications develop, it’s important to know the signs and symptoms of bruxism and to seek regular dental care.
Signs of Bruxism
Symptoms may include:
- Teeth grinding or clenching
- Teeth that are flattened, fractured, chipped or loose
- Worn tooth enamel, exposing deeper layers
- Increased tooth sensitivity
- Jaw or face pain or soreness
- Tired or tight jaw muscles
- Pain that feels like an earache
- Dull headache originating in the temples
- Damage from chewing on the inside of your cheek
- Indentations on your tongue
- Bleeding gums, receding gum line
- Loose teeth
- Periodontal pockets
See your doctor or dentist if:
- Your teeth are worn, damaged or sensitive
- You have pain in your jaw, face or ear
- Others complain that you make a grinding noise while you sleep
- You have a locked jaw that won’t open or close completely
If you notice that your child is grinding his or her teeth — or has other signs or symptoms of bruxism — be sure to mention it at your child’s next dental appointment.
What Causes Bruxism?
Doctors don’t completely understand what causes bruxism. Possible physical or psychological causes may include:
- Emotions, such as anxiety, stress, anger, frustration or tension
- Aggressive, competitive or hyperactive personality type
- Abnormal alignment of upper and lower teeth (malocclusion)
- Response to pain from an earache or teething (in children)
- An uncommon side effect of some psychiatric medications, such as phenothiazines or certain antidepressants
- A coping strategy or focusing habit
- Complication resulting from a disorder such as Huntington’s disease or Parkinson’s disease
These factors increase your risk of bruxism:
- Stress. Increased anxiety or stress can lead to teeth grinding. So can anger and frustration.
- Age. Bruxism is common in young children, but it usually goes away by the teen years.
- Personality type. Having a personality type that is aggressive, competitive or hyperactive can increase your risk of bruxism.
- Stimulating substances. Smoking tobacco, drinking caffeinated beverages or alcohol, or taking illegal drugs such as methamphetamines may increase the risk of bruxism.
Severe bruxism may lead to:
- Damage to your teeth, restorations, crowns or jaw
- Tension-type headaches
- Facial pain
- Disorders that occur in the temporomandibular joints (TMJs), located just in front of your ears, which may sound like clicking when you open and close your mouth
During regular dental exams, your dentist likely will check for signs of bruxism. If you have any signs, your dentist will look for changes in your teeth and mouth over the next several visits to see if the process is progressive and to determine whether you need treatment.
If your dentist suspects that you have bruxism, he or she will try to determine its cause by asking questions about your general dental health, medications, daily routines and sleep habits.
To evaluate the extent of bruxism, your dentist may check for:
- Tenderness in your jaw muscles
- Obvious dental abnormalities, such as broken or missing teeth or poor tooth alignment
- Damage to your teeth, the underlying bone and the inside of your cheeks, usually with the help of X-rays
- Strength of masseter muscles or jaw
If you or your child has bruxism, your doctor may suggest ways to preserve or improve your teeth. Although these methods may prevent or correct the wear to your teeth, they may not stop the bruxism:
- Splints and mouth guards. These are designed to keep teeth separated to avoid the damage caused by clenching and grinding. They can be constructed of hard acrylic or soft materials and fit over your upper or lower teeth.
- Dental correction. Correcting teeth that aren’t properly aligned may help if your bruxism seems to be related to dental problems. In severe cases — when tooth wear has led to sensitivity or the inability to chew properly — your dentist may need to reshape the chewing surfaces of your teeth or use crowns. In certain cases, your dentist may recommend braces or oral surgery.
Certain therapies may help relieve bruxism, such as:
- Stress management. If you grind your teeth because of stress, you may be able to prevent the problem with professional counseling or strategies that promote relaxation, such as exercise or meditation.
- Behavior therapy. Once you discover that you have bruxism, you may be able to change the behavior by practicing proper mouth and jaw position. Ask your dentist to show you the best position for your mouth and jaw.
Medications
In general, medications aren’t very effective for treatment of bruxism, and more research is needed to determine their effectiveness. Examples of medications that may be used for bruxism include:
- Muscle relaxants. In some cases, your doctor may suggest taking a muscle relaxant before bedtime, for a short period of time.
- OnabotulinumtoxinA (Botox) injections. Botox injections may help some people with severe bruxism who don’t respond to other treatments.
If you develop bruxism as a side effect of a medication, your doctor may change your medication or prescribe a different one.
These self-care steps may prevent or help treat bruxism:
- Reduce stress. Listening to music, taking a warm bath or exercising can help you relax and may reduce your risk of developing bruxism.
- Avoid stimulating substances in the evening. Avoid stimulants. Don’t drink caffeinated coffee or caffeinated tea after dinner, and avoid alcohol and smoking during the evening, as they may worsen bruxism.
- Practice good sleep habits. Getting a good night’s sleep, which may include treatment for sleep problems, may help reduce bruxism.
- Schedule regular dental exams. Dental exams are the best way to identify bruxism. Your dentist can spot signs of bruxism in your mouth and jaw with regular visits and exams.
Laser Dentistry
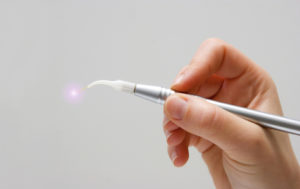 A laser in an instrument that produces a very narrow, intense beam of light energy. When laser light comes in contact with tissue, it causes a reaction. The light produced by the laser can remove or shape tissue.
A laser in an instrument that produces a very narrow, intense beam of light energy. When laser light comes in contact with tissue, it causes a reaction. The light produced by the laser can remove or shape tissue.
Lasers have been used in dentistry since 1990. Lasers can be used as a safe and effective treatment for a wide range of dental procedures and are often used in conjunction with other dental instruments.
Dental lasers can be used to:
- Reduce discomfort of canker and cold sores.
- Expose partially erupted wisdom teeth
- Remove muscle attachments that limit proper movement
- Manage gum tissue during impressions for crowns or other procedures
- Remove overgrown tissue caused by medications
- Perform biopsies
- Remove inflamed gum tissues and aid in treatment of gum disease
- Remove or reshape gum and bone tissues during crown lengthening procedures
- Help treat infections in root canals
- Remove/treat bacterial in gingival pockets surrounding teeth
Laser procedures are precise. Also, lasers can reduce symptoms and healing times associated with traditional therapies; reduce the amount of bacteria in both diseased gum tissue and in tooth cavities; and control bleeding during surgery.
If the laser is used according to accepted practices by a trained practitioner, then it is at least as safe as other dental instruments. However, just as you wear sunglasses to protect your eyes from prolonged exposure to the sun, when your dentist performs a laser procedure, you will be asked to wear special eyeglasses to protect your eyes from the laser.
Although the laser is a very useful dental instrument, it is not appropriate for every dental procedure.
Dental Pulp Diseases: The Basics
Poor oral health can lead to pulp diseases that require root canals, or worse. Learn about the types, symptoms, and treatments for oral pulp diseases.
Don’t Miss This
Poor dental hygiene is the main reason for tooth decay, tooth pain, and other oral health conditions. If you don’t maintain good oral health habits, including brushing and flossing regularly, plaque can develop and lead to cavities. Left untreated, a cavity can eventually affect the soft center (or pulp) of your tooth, which contains sensitive nerves and delicate blood vessels. And if pulp diseases aren’t properly managed, you can lose your teeth.
 Symptoms of Pulp Diseases
Symptoms of Pulp Diseases
Depending on the type of pulp disease, symptoms may vary in intensity and can include:
- Pain in a tooth or teeth when you eat something very sweet, hot, or cold
- Sudden, intense pain in the mouth
- Infection in the mouth
Types of Pulp Diseases
There are several different pulp diseases, including:
- Reversible pulpitis, or mild inflammation of the pulp. Symptoms typically include pain upon eating or drinking something very sweet, hot, or cold. Without treatment, the inflammation can progress to a dental abscess, a collection of bacteria and pus. Good oral health habits can help offset reversible pulpitis, but in many cases, a filling is eventually needed. Pulpitis can also occur if you crack or break a tooth.
- Irreversible pulpitis, or severe inflammation of the pulp that can’t be cured. Symptoms include sudden intense pain. Left untreated, it can result in a widespread gum and connective tissue infection. Irreversible pulpitis is generally treated with a root canal procedure. If that doesn’t work, your dentist may have to remove the tooth.
- Dental pulp calcification (also known as dental pulp stones). This is a condition in which hardening, or calcification, of pulp tissue results in hypersensitivity and extreme pain because the dental nerves become compressed. A root canal is usually necessary to clear away hardened tissue.
- Dental pulp exposure. This condition comes on when damage to the external covering of a tooth, such as a cavity or crack in the tooth, exposes the normally protected pulp to bacteria and irritating food particles. Pain is the most frequent symptom and without proper dental care, a mild infection can progress into a serious abscess. Depending on the degree of pulp exposure, a filling, root-canal procedure, or even tooth extraction may be required.
Pulp Diseases Treatment: Root Canal Therapy
If damaged pulp in your tooth isn’t taken out, a severe infection can spread to surrounding tissue, including your jaw bone. A root canal procedure to remove the pulp tissue is usually performed over several visits by a regular dentist or a pulp specialist, called an endodontist. The root canal therapy may spare you from having to get the infected tooth removed.
Here’s what you can expect from root canal therapy:
- First visit. The diseased pulp is removed and the empty space, the root canal, is cleaned out and enlarged. Special medications may be placed in the canal to disinfect the area. A temporary filling may be placed as well, or your dentist may choose to leave the canal open and let the tooth drain for a few days. An oral antibiotic may also be recommended to treat infection in the tissues surrounding your tooth.
- Second visit. The temporary filling is removed and a permanent filling is placed.
- Final visit. A crown is placed over the tooth to reinforce the tooth and make it stronger.
Some pulp diseases may be caused by an injury that broke a tooth. But many other pulp diseases are simply caused by poor oral health habits. If you brush and floss regularly and seek out regular dental care, you are less likely to develop pulp diseases.
Dental Health and Overall Health
 Healthy mouth, healthy body.
Healthy mouth, healthy body.
The condition of your mouth is closely tied to your overall health. Oral health is linked to diabetes, heart disease, cancer, and more.
Taking care of your teeth isn’t just about having a nice smile and pleasant breath. There are a number of links between oral health and overall health. The condition of your mouth is closely tied to your overall physical health.
Oral Health and Diabetes
Type 2 diabetics have an increased incidence of periodontitis, or gum disease. While more research is needed before doctors can conclude that gum disease actually leads to diabetes, there are already a few theories about why this might be the case. One proposes that when infections in your mouth get bad enough, they can lead to low-grade inflammation throughout your body, which in turn wreaks havoc on your sugar-processing abilities.
Oral Health and Heart Disease
As with diabetes, the connection between poor oral health and cardiovascular conditions has been recognized — the two are often found together — but it still hasn’t been determined conclusively whether or not there is a direct causal relationship between them. “Bad” bacteria from an infected mouth may lodge itself inside blood vessels, ultimately causing dangerous blockages. Strengthening his theory is the fact that when scientists have looked at atherosclerotic blood vessels, they have sometimes found fragments of periodontal bacteria. Meanwhile, a study published in the New England Journal of Medicine in 2007 established that aggressive treatment of gum disease reduces the incidence of atherosclerosis within six months.
Pregnancy Complications and Gum Disease
For many pregnant women, gum infections stem from the fluctuating hormone levels that come with pregnancy. Others neglect their oral care during pregnancy, since they have much on their minds. Calcium to the mother can be depleted during a pregnancy as it is being pulled by the fetus. Scientists believe that gum disease or inflammation in the mouth possibly triggers an increase in a chemical compound called prostaglandin, which induces early labor. Regular dental visits are imperative to maintain dental health during a woman’s pregnancy.
Embarrassing Oral Health Problems…Solved!
Stinky breath, unsightly mouth sores, and tooth decay: we’ve got a solution for all of your dental-health dilemmas.
What is the best way to keep your mouth, teeth, and gums looking and feeling great? Your daily brushing and flossing routine, combined with a balanced diet and regular dental visits.
However, following these oral hygiene rituals isn’t always enough. Many common oral-health problems, such as bad breath, tooth decay, erosion, receding gums, and mouth sores, can leave people feeling both physically uncomfortable and reluctant to smile. Fortunately, with the right treatments these embarrassing oral-health problems can be solved!
Bad Breath
Treatment for bad breath, or halitosis, varies depending on the cause. Brushing and flossing is crucial since it helps keep food particles from collecting bacteria and decaying in your mouth. If your dentist gives you a clean bill of health, you will need to investigate further. Your bad breath could be the result of a medical disorder, such as a respiratory infection; chronic sinusitis or bronchitis; diabetes; a gastrointestinal disturbance, such as GERD; or a liver or kidney ailment. The use of particular medications can cause dry mouth, which can contribute to bad breath. And sometimes, the solution may be as simple as changing your diet: If you are a garlic or onion lover, cutting down on these foods will help. Eliminating tobacco if you’re a smoker will help as well.
Tooth Decay and Erosion
Brushing twice a day with fluoride toothpaste, flossing once a day, and visiting your dentist regularly for exams and cleanings will help fight tooth decay and erosion. Your dentist may also recommend protective plastic sealants to reduce your risk of decay. Eating a balanced diet and keeping your “junk food and sweets” to a minimum will also help head off plaque and erosion. If you’re particularly concerned about erosion, avoid acidic food and drinks, such as citrus fruits and juices, tomatoes, pickles, soda, and sports drinks. Studies suggest that they can strip enamel from the teeth. Gastric acid can also contribute to erosion, so if you have a medical condition like acid-reflux disease or bulimia, getting treatment is imperative.
Receding Gums
Gum recession and periodontal disease can have serious repercussions. Early stage gingivitis causes the gums to become red and swollen, and to bleed easily. The more advanced periodontitis damages the gums and bones that support the teeth, causing them to loosen and fall out. Gum recession can also result from aggressive tooth brushing with medium or hard bristles, mal-positioned teeth, or bad habits such as clenching, grinding, or scratching your gums with foreign objects. You can also help protect your gums by using an ultrasoft toothbrush and wearing a night guard to reduce stress on your teeth if you tend to clench or grind at night
Mouth Sores
Canker sores and cold sores are two of the most common sores that show up around the mouth. They can be painful, annoying, and unsightly. Cankers develop inside the mouth, while cold sores appear externally, usually on the edge of the lips. Fortunately, both of these types of sores tend to heal on their own within a week or so, and canker sores can be treated with over-the-counter topical anesthetics or antimicrobial mouth rinses to reduce discomfort. Topical anesthetics may also provide temporary relief for cold sores. If you’re embarrassed by frequent cold-sore outbreaks, talk to your doctor about getting a prescription for antiviral drugs that could help reduce infections from the herpes virus.
